Certifications
-
 ISO 9001:2015
ISO 9001:2015 -
 EN 1090-2 (DVS)
EN 1090-2 (DVS) -
 DIN EN ISO 3834-2 (TÜV)
DIN EN ISO 3834-2 (TÜV)


Microtrenching is a minimal-destructive and very fast method of laying communication cables in existing traffic areas. In the process, wide joints are cut into the surfaces with diamond blades. Directly after the cut, ductworks are inserted and then the joint is potted. Time and cost-intensive earthworks at the edge of the traffic areas are thus avoided or minimized.
With microtrenching machines based on the new fully hydraulic RSF 820 floor saw, RELLOK provides the necessary special equipment for the application of this future-oriented cable laying technology.
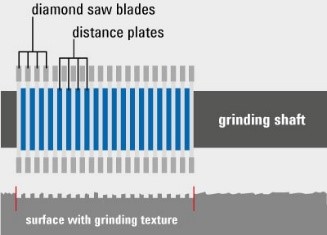
With grinding and grooving, defined textures and groove profiles are made into the surface. Regardless of the given road surface, the grinding profile must always be the same depth. This is the only way to ensure the desired function (e.g. water drainage) throughout. With bump cutting, no groove profile is created, but a new road surface is created by grinding. With RELLOK bump cutters this is achieved as follows:
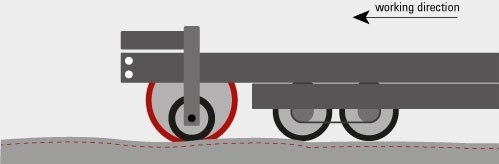
The front wheels are arranged in line with the grinding shaft. Depending on the desired grinding depth, the shaft is lowered below the level of the front wheels and fixed. During the work process, the front wheels and thus the grinding shaft follow the existing road structure exactly. The grinding depth remains constant.
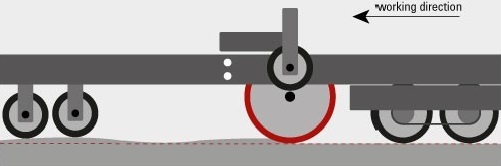
With bump cutting, the front wheels are mounted at a greater distance in front of the grinding shaft. Due to the long lever arm, the road surface no longer has any relevant influence on the vertical movement of the cutting shaft. The road surface is grinded down to the preset depth and bumps are removed. Depending on the design of the bump cutter, this function is already integrated or can be achieved with a corresponding attachment frame.
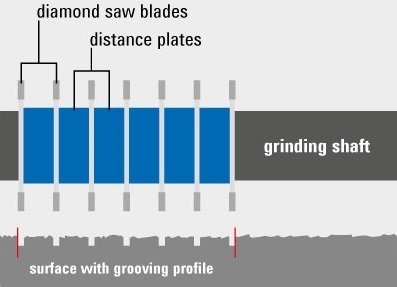
Surface grinding using a shaft setting without spacers is also called bump cutting. This smooths out any unevenness that may arise in the manufacturing process or as a result of surface wear. By inclining the grinding shaft, the method can also be used to adjust small height differences (edges) between surfaces.

The cutting of grooves to drain water in traffic areas is called grooving. In addition to roads, this method is also used on air traffic areas. In addition to the improved drainage of flowing water, the road surface also dries faster due to the enlarged surface.
Grinding is used to produce a defined roughness of the surface in order to ensure the “grip” required for vehicles. Another application is the so-called acoustic grinding. Here, the shaft-saw blade configuration is chosen so that a special grinding pattern is created to reduce road noise.